Can Augmented Reality Improve the Learning Experience of Future Healthcare Professionals? (2022)
Posted on 7/1/22 by Maite Suarez-Rivas
Did you know that a 2022 survey revealed that many of today’s high school students want to be tomorrow’s healthcare professionals? When asked to list their top ten desired career fields, 27% of students polled by the National Society of High School Scholars said they wanted to pursue a medicine or health-related career, and 20% selected the healthcare field more broadly.
Ready for the not so great news? A 2017 survey concluded that more than a quarter of students who enter college pursuing a healthcare degree will change their major.
Why do students stop pursuing science degrees? Students find the coursework in science fields to be tough; it can be too abstract, certain concepts can be hard to visualize, and one misconception can lead to another and another—resulting in a student who is lost and too far behind to catch up.
This might be why instructors are forever on the hunt for new ways to improve performance and keep students interested. For instructors around the world, one solution is augmented reality (AR).
How does augmented reality improve student learning?
AR has a few features in common with other successful technologies instructors use, like 3D apps, multimedia games, even PowerPoint presentations and animations:
- It offers the type of collaborative learning that engages students.
- It helps with the development of spatial skills needed to understand three-dimensional objects (like anatomical structures).
- Multimedia like AR puts the student in the driver's seat and can build student understanding and confidence to learn on their own.
This list, summarized from Christopher Cerqueira's Developing Educational Applications with a Non-Programming Augmented Reality Authoring Tool, focuses on how the visualization and interactivity offered by augmented reality enhances students' experience:
- Using the technology motivates students
- AR helps students see what they can't with the naked eye
- AR provides detailed visualization
- Students can get views at many angles and sizes
- Instructors can create virtual experiments
- Students can use AR to study when not in lab
- Students are moving around and active in class
- The AR experience encourages curiosity
- AR accommodates different learning styles
- Spatial visualization and understanding is improved
Educause’s HP Campus of the Future project published its Year 2 report in October of 2019. Overall, they found that XR (AR, VR, and MR technologies) are most effective in the classroom when they:
- Support “skills-based and competency based teaching and learning, such as nursing education, where students gain practice by repeating tasks”
- Make it so that abstract concepts usually taught using illustrations or videos can be learned in a skills-based way
- Provide functionalities and forms of interaction that are not available through more traditional educational methods
When it comes to achieving learning goals, the report also highlights the importance of “fidelity, ease of use, novelty, time-on-task, and the spirit of experimentation.” All in all, AR has the potential to use these characteristics to increase student engagement and encourage self-directed learning.
VB Suite for iPhone, iPad, and Android devices creates an anatomy lab experience anywhere there is a flat surface.
What evidence shows that AR improves student learning?
A large anatomy-focused augmented reality study was conducted in 2015 at the Ludwig-Maximilians Universität in Munich, pairing AR learning activities with a traditional cadaver lab. The technology allowed students to see diagnostic images in augmented reality. Out of the 850 first-year medical students that took part in the research, a little over 80% reported that the AR tool increased learning motivation and 93% said it increased their spatial understanding of anatomy.
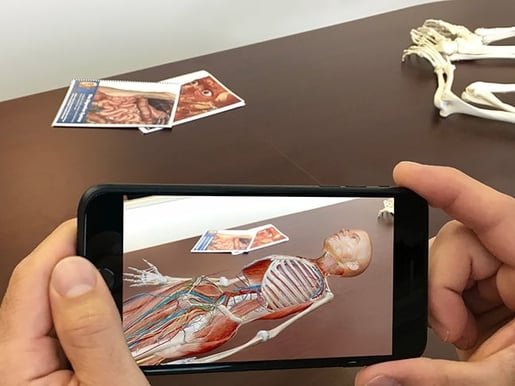
AR mode in Visible Body Suite.
A smaller anatomy-focused augmented reality study was conducted in 2015 with a few dozen undergraduate science students from three universities. The students were split into two groups. Both received some skeletal anatomy presentations. One group studied with traditional methods and a second group used an augmented reality skeletal model created for the study. A test was administered to both groups. Results showed that the second group performed almost twice as well as students in the first group.
This 2012 paper in the International Journal of Computer Applications shares how computer science students at the Jaypee Institute of Information Technology built an augmented reality system to teach high school students molecular chemistry. Their first goal was to build an AR lesson tool that replaced the 2D representations of molecule models in books and PowerPoints with 3D models in AR. The second goal was to replace the way molecular structures were taught. Rather than ask students to read descriptions or listen to a lecture, they were encouraged to work with the 3D models in AR and collaborate with other students. The paper concludes that students gained more knowledge of molecular structures, improved their spatial intuition, and better understood visual cues.
These results highlight a common theme: augmented reality is motivating and better enables students to learn the spatial relationships that are critical to understanding the human body.
How can AR engage students in the “post-pandemic classroom”?
To put it lightly, a lot has changed since this article was originally published in 2018.
We talk to a lot of life sciences instructors, and we’ve heard many say that, after a substantial time doing remote learning, students are having difficulty adjusting to the classroom environment. Students are struggling to stay engaged.
As Chronicle of Higher Education writer Beth McMurtrie points out in the magazine’s April 2022 cover story “A ‘Stunning’ Level of Student Disconnection,” today’s students are dealing with an increase in social anxiety, family distress, and downright dread. As a result, “their brains seem to shut off” in the classroom.
AR can reinvigorate the classroom, generating excitement among students and encouraging engagement in course content. More engagement allows students to take a more active role in their learning.
Multiple studies have indicated that augmented reality increases student engagement and interest in learning. For example, a review of augmented reality usage in medical education literature found that not only does AR increase learning outcomes like professional knowledge, but it also boosts more unexpected outcomes like creativity and innovation.
Put simply, students get excited about AR!

AR mode in VB Suite .
A study of 171 medical, physiotherapy, and podiatry students found that the majority—even the students who were not in the AR group—thought that AR was a positive tool for learning. About 77% of the students thought that AR would be effective for studying, while about 67% thought that their grades would improve if their professors used AR.
A paper published in 2020 studied 90 postgraduate students from an Australian university. After a lesson and an AR/VR session, students were asked to write a reflection on their experience. The majority of student reflections mentioned an increased level of engagement: students talked about how AR connected to their interest in the subject matter and their overall enjoyment of the experience, mentioning fun and excitement in addition to the unique sensory experience of simultaneously interacting with the real world and the digital world.
This is corroborated by a study published in Advances in Human-Computer Interaction in February 2019, which showed an increase in student motivation as a result of using an AR application. In this study, researchers from the University of Cape Town analyzed the use of an AR mobile application on 78 health science undergraduate students in an anatomy course.
The students completed a pre-usage questionnaire and a post-usage questionnaire, which evaluated their experience based on Keller’s “ARCS” (attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction) model of motivational design.
Ultimately, the results showed that using the AR mobile application increased students’ motivation by 14%. Students experienced a 31% increase in attention, an 11% boost in confidence, and a 13% increase in satisfaction. Their answers to the questionnaire indicated a 3% decrease in relevance, but this was found to be statistically insignificant.
How does increased motivation help students? The authors of the study say that, based on previous research, “students that are academically motivated tend to engage, persist, and expend effort to complete tasks compared to unmotivated students.” They also add that “a lack of motivation could be a major obstacle to learner success.”
Essentially, what it comes down to is that more engaged students are more academically successful, and AR is a good way to increase the motivation that drives engagement.
Is augmented reality just a trend?
Augmented reality is here to stay! An estimated 1.07 billion people currently use mobile AR apps—a number that is expected to grow by 6.6 million in the next two years. Instructors have used AR learning tools for well over a decade, and they have noted their educational benefits.
Historically, AR has required special computers, eyewear, and often expensive software that instructors needed to create an AR student experience, but the popularity of smartphones and other mobile devices means that AR is right at your fingertips.
Augmented reality is available on devices that schools already own and students often carry 24/7! Software developers have released everything from My Very Hungry Caterpillar for preschoolers to human body content like our own Visible Body Suite.
One final reason why AR is quickly becoming the norm: use by healthcare professionals for diagnosis and patient education is on the rise. So is investment in developing new AR/VR healthcare technologies. The more comfortable students are with this emerging healthcare technology, the better prepared they'll be when they come across it in their future careers.
Be sure to subscribe to the Visible Body Blog for more anatomy awesomeness!
Are you an instructor thinking about using AR in your classroom? If you've got questions, or if you're interested in a demo, get in touch with our education team! Learn more here.



